Parts of speech are the basic types of words that English has. It is compulsory to recognize and identify the different types of words in English so that we can understand grammatical explanations and use the right word in the right place.
By using proper grammar in writing and speaking, you will be able to communicate clearly and dynamically with your subject or audience! What’s more, you’ll be able to master grammar by learning and comprehensively understanding the parts of speech.
But! when we talked about parts of speech, the first question that comes to our mind is! what is the speech?
What is speech?
“The ability to express your thoughts, emotions, and feelings through vocal sounds is called speech.”
What are parts of speech?
“A part of speech is just the name given to a word based on the job that it does in a sentence.”
“Words that do more than one job are known as parts of speech.”
 More precisely words are considered the smallest ingredients.Put simply, it’s like we make Biryani and add some spices to it and named all those spices and ingredients accordance to their taste. Likewise, we call parts that are used in English, parts of speech because words are considered the smallest ingredients that we used to make a sentence.
More precisely words are considered the smallest ingredients.Put simply, it’s like we make Biryani and add some spices to it and named all those spices and ingredients accordance to their taste. Likewise, we call parts that are used in English, parts of speech because words are considered the smallest ingredients that we used to make a sentence.
It’s quite significant to acknowledge parts of speech. This’ll help you to analyze sentences and understanding them and it also helps you to make competent and dynamic sentences. Based on their use and functions, Parts of speech are categorized into 8 basic types.
Why are the parts of speech important?
Some grammar sources generally categorize English into 9 parts of speech, others say 10 but Litenglishers use the more recent categorization of 8 parts of speech.
To show you what I mean!
Determiners ( a, an, The ) may be treated as a separate part of speech, instead of considered to be a part of an adjective.
Many words in English perform more than one job and also be more than one part of speech.
For instance :
| Work | can be a noun, verb & sometimes Adjective | Noun
verb |
My work is easy.
I work in Pakistan. |
| But | can be conjunction & a preposition | Conjunction
Preposition |
Hania came but Aila didn’t come.
Everybody came but Ali is in the room. |
| Afternoon | can be a noun & sometimes act as an adjective | Noun
adjective |
We ate in the afternoon.
We had afternoon tea. |
| well | can be an adjective, an adverb, and also an interjection | Adjective
Adverb Interjection |
Are you well?
She eats well. Well, that’s immoderate. |
| To | can function as a noun, Adjective, preposition or Adverb | Preposition
Noun Adjective |
Does this bus go to Karachi?
The door to the main gate was open. Saima is used to working on a tough assignments. |
Parts of speech indicate how the word functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence. An individual word can function as more than one part of speech when used in different circumstances. To analyze the parts of speech ask yourself what job the word you are used to doing in this sentence.

8 Parts of speech:
- Noun
- Pronoun
- Adjective
- Verb
- Adverb
- Conjunction
- Preposition
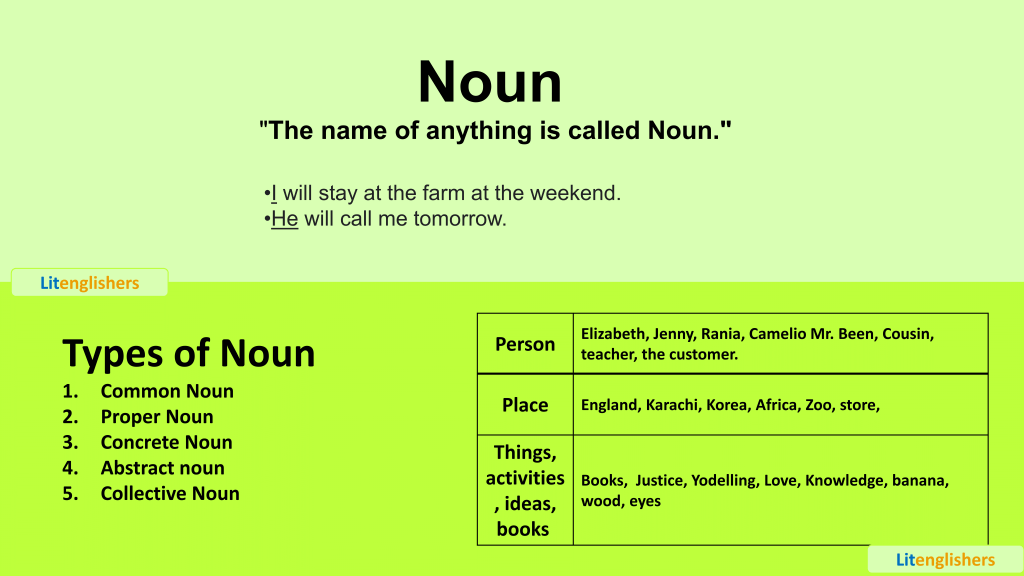
1:Noun and its types
“The name of anything is called Noun.”
In simple words,The things that belong to the world are considered to be a Noun. It could be anyone whether you are talking about a human, animal, angel, ghost, bird, insects, love, hatred, friendship, self-preservation or Helen.
It’s like the bread and butter of our speech.
| Person | queen Elizabeth, Helen, Rania, Cousin, teacher, the customer. |
| Place | America, Saudi Arabia, Switzerland, Africa, Zoo, store, Hospital |
| Things, activities, books books | Notes, Patience, Love, Knowledge, banana, wood, eyes |
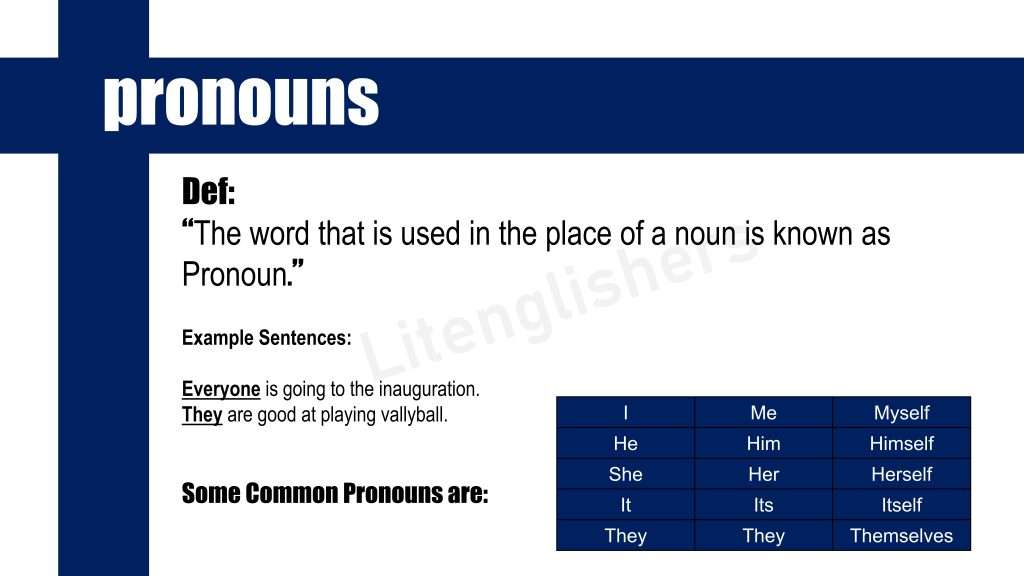
2: Pronoun and its Types
Pro +Noun
Pro means “For”and Noun means “Name”
“The word that is used in the place of the noun is called Pronoun.”
For Example:
He, h e, it, they, we, you.
| Sentences | Use of Pronoun in the sentence |
| we have built a car. | we |
| She goes to work everyday. | She |
| I am gonna hit you. | i |
3: Adjective and its types
“The word that modifies a noun is known as Adjective.”
“(naming a hallmark to a not
Basically, it expresses, demystify, modifies,demonstrate, tells us more, or gives more information about a noun. Skimpily it comes before a noun.
For Example:
- He is a good boy.
- She is a Chubby girl.
| Rules | Example sentences |
| Frequently it comes before noun | A Beautiful house. |
| Adjective comes after a verb | The sky becomes dark. |
| It can also modify pronouns. | Those are not expensive. |
| sometimes we use more than one Adjective together | A beautifulteen-aged African lady. |
Adjectives that come before the noun are known as “attributive adjective.”
Adjectives that come after the noun are known as “predicate adjective.”

4: Verb and its kinds
“A word or a group of words that is used to indicate actions.”
Word stands for doing or being something used to convey or represent actions and conditions. A sentence may either have a main verb, a helping verb, or both.
For Example:
| Action | State of Being |
| She ironed her dress. | She feels tired. |
| ↑ verb |
↑ verb |
5: Adverb and its types
“The word that modifies a verb, adjective, or itself.”
Basically, it tells about the verb, in which intensity of the action takes place. It tells how, where, when, how often, or to what extent something is done.
For Instance:
- The alarm rang loudly.
- They go out to dinner weekly.
In the sentence “weekly“ is a verb, and “loudly” is an adverb so it tells in what intensity the alarm rang.

6: Conjunction
“A word that is used to connect words, expressions, clauses, and phrases.”
Put it simple, it connects elements of a sentence at the same point in time or space.
For Example:
out, or, although, but, when, which, and.
- He would rather play than work.
- The flower is red and it smells like a pearl.
And & than are conjunctions that connect two clauses or phrases together.

7:Preposition and its types
Pre+Position
“The word that describes position and relationship between two parts of a sentence.”
Generally, it is a word or set of words used before a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to disport direction, time, place, location, relationships or to introduce an object.
For Example: such as, in, above, across, beyond, beneath, up
- The book is on the table.
- He hides under the chair.
On & under is a preposition.

8:Interjection and its types
“A word that shows unconscious or sudden feelings and emotions.”
For Example: your sudden reactions like Hurrah!, Alas!, Aww, Ouch, Oops!.
- Hurry! we get it.
- Aww! you are so sweet.
- Oops! I miss the chance.
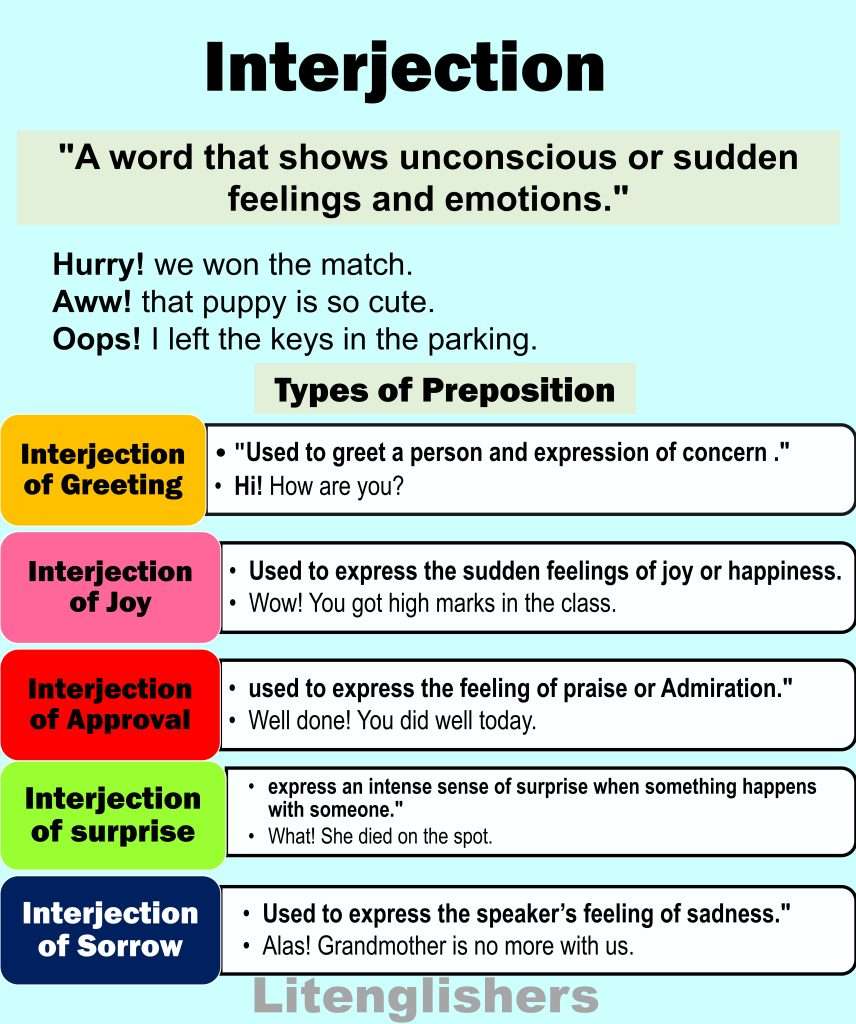
Note: They are not connected to the rest of the sentence and commonly end with the exclamation mark (!) and with commas (,).
What are Open and closed word classes?
Parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determinants, and interjections).
The idea is that open classes can be changed and added to as the language evolves, and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
Are you using the correct part of speech? Check your grammar and find out!
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
Parts of speech and their Types in detail