Conjunction /kənˈdʒʌŋ(k)ʃ(ə)n/
“A word that is used to connect words, expressions, clauses, and phrases is known as a conjunction.”
A word that brings parts of a sentence together is work as a conjunction. Conjunctions can be small words like (or, but, and), or they can be big words like (because, although, or whenever), size doesn’t matter because conjunctions make your writing and your words more interesting. It connects elements of a sentence.
For Example:
- He would rather read novels than study books.
Although he was tense, he went to school daily.
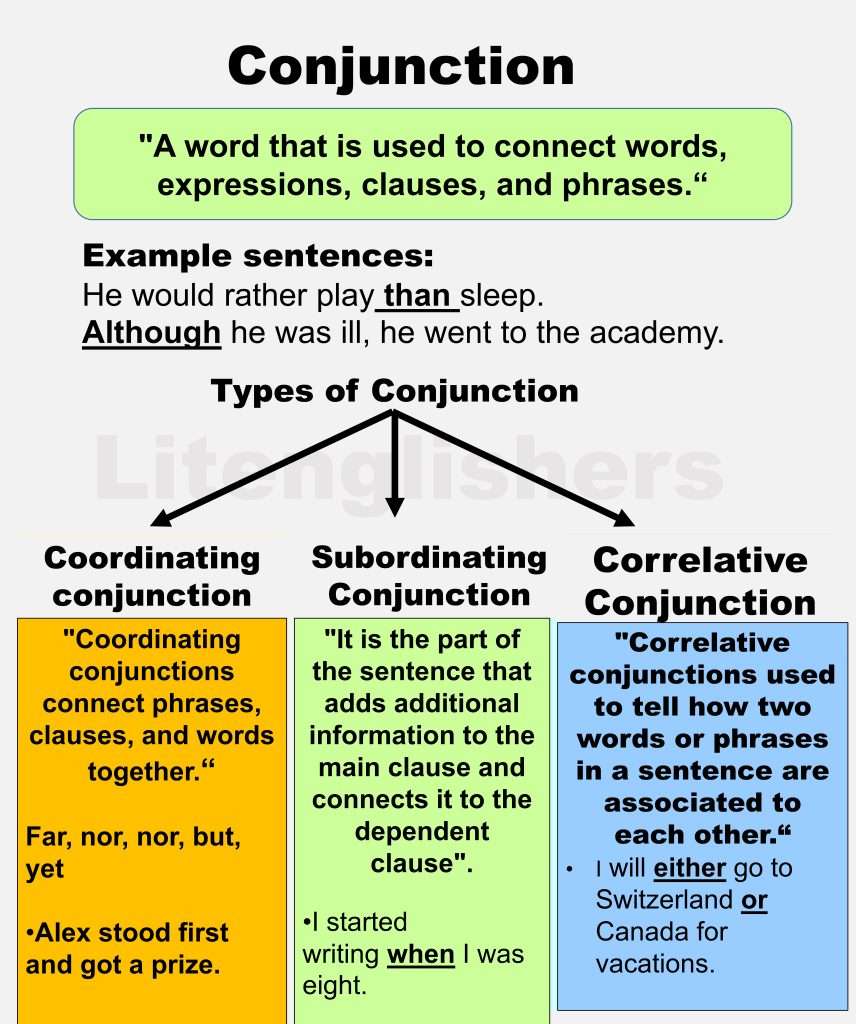
Types of Conjunction
Instead of speaking simple sentences, use conjunctions in every sentence. Conjunctions are a great tool to have.
- coordinating conjunctions
- subordinating conjunctions
- correlative conjunctions
1 Coordinating Conjunctions
“They used to connect phrases, clauses, and words.”
The seven coordinating conjunctions are pretty easy to memorize with this simple trick. You just remember a single word (FANBOYS ) “For, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.” .so overall these words are coordinating conjunctions. The seven coordinating conjunctions can be used as both coordinating conjunction and subordinate conjunction. Coordinating conjunction (so) can join two independent clauses in a similar, therefore, and as a subordinating conjunction, it can join two unequal clauses, one independent and one dependent in the sense like so that.
| Coordinate conjunction | Subordinate conjunction |
| We were out of fruits, so I went to the store to buy some fruits. | Alisha is saving money so she can buy her own house. |
For Example: words like, who, an, yet, but, or, so, for,nor, and besides, nevertheless are used to coordinate clauses and phrases.
- Ali stood first in the class and got gold meddle.
- Robina and Raees went to the market.
- Sleep now or you will miss the chance tomorrow.
- Rameen did not try hard so he did’t get the expected marks.
- He is sad but not hardhearted.
- Rikza, as well as Swaira, came here yesterday.
- Shushan played well still he win the game.
- I bought banana and butter.
- We can walk or drive to the house.
- Payal was late for college,so she took a shortcut.
2: Subordinate conjunction
“Subordinate conjunctions use to add additional information to the main clause and connects it to the dependent clause”.
- Subordinating conjunctions can be found in sentences containing two clauses an independent clause and a dependent clause.
- They usually come at the beginning of a dependent clause.
- They gave meaning to a sentence by linking two ideas time, concession, comparison, cause, condition, and place are the types of subordinate conjunctions.
- In most sentences, as long as the subordinating conjunction anticipate the dependent clause but there clause order does not matters the most.
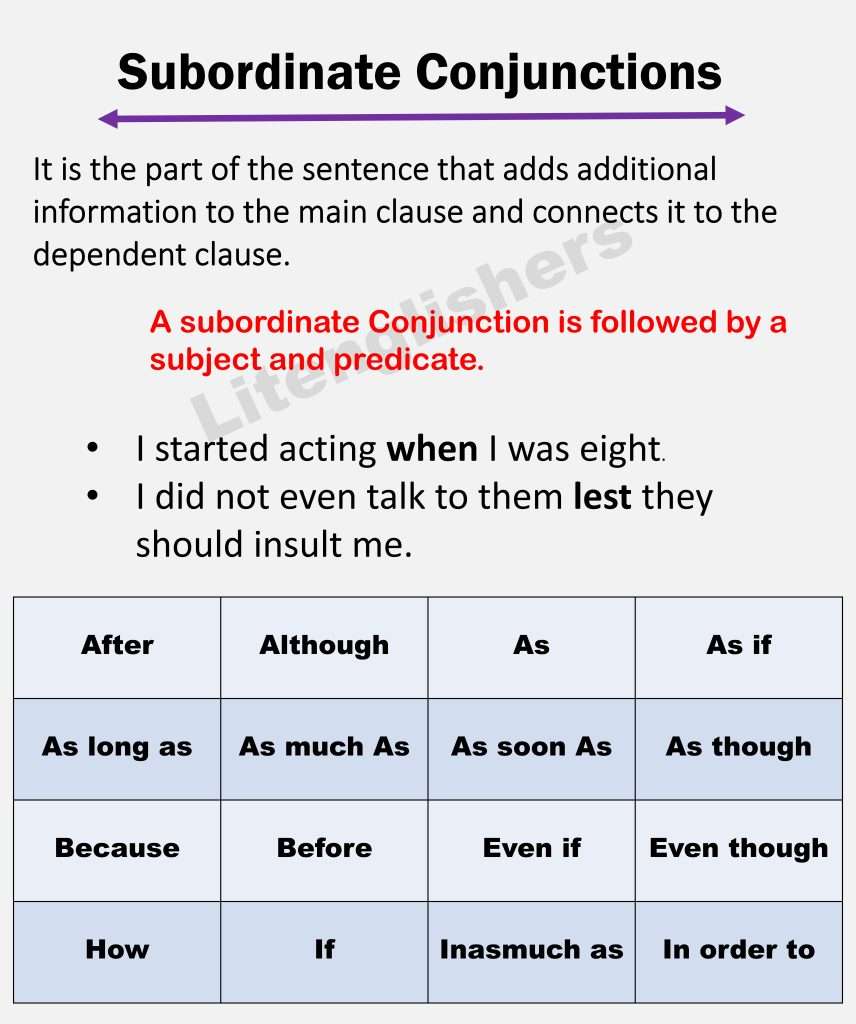 Subordinating conjunctions are also known as subordinators or subordinate conjunctions, and complementizers. Many subordinators are single words such as (because, before, and when, but). some subordinating conjunctions consist of more than one word such as (even though,as long as, and except that.
Subordinating conjunctions are also known as subordinators or subordinate conjunctions, and complementizers. Many subordinators are single words such as (because, before, and when, but). some subordinating conjunctions consist of more than one word such as (even though,as long as, and except that.
Example Sentences:
- He will always support me whether I get good marks or not.
- I started writing when I was twenty years old.
- Everyone asked me how I wrote such novels at this age.
- I did not understand why people tried to tease others.
- I did not feel good about it as I never express my feelings.
- I did not have so many friends until I was admitted to university.
- I used to sit alone and think about many things while others play with their friends,
- I did not even talk to them lest they should abuse me.
Semantic Categorization of Subordinating Conjunctions
As explained, conjunctions can bring different layers of meaning to writing by building relationships between clauses. There are six main classes of conjunctions that are categorized by meaning: (time, concession, comparison, cause, condition, and place.)
i: Time
Time related conjuncti0ns complete a period when the main clause will be or was performed. These sentences includes (after, as soon as, as long as, before, once, still, until, when, whenever, and while.)
For example:
- I will do the household cores after everyone has gone home” might be stated a hostess who prefers to enjoy her guest’s company while they are there.
Concession conjunctions help to map out the main clause by binding context regarding conditions of delivery. Concession conjunctions highlight an action that took place besides any barrier or block and they include (although, as though, and even though.)
For Example:
- Fiza wrote the Canadian report even though it was assigned to Colonel Pickering.
iii: Comparison
Alternatively, comparison conjunctions include (just as, though, whereas, in contrast to, and while) that help to substantiate correlations by providing context for comparison.
Example sentence:
- Emaan wrote a vlog about the results of the president meeting, as compared to her buddy who solely blogged.
iv: Cause
Cause conjunctions find out the reasons that the activities of the main clause were carried off and are commonly engineered using as, because, so that, since, and so that.
For Instance:
- German dreamed about cake because he had eaten so much of it the night before.
v: Condition
Condition conjunctions initiate the rules under which the main clause performs. These are indicated by even if, if, in case, provided that, and unless. Like
- If he’s going to be there, I’m not going to the inauguration.
Sometimes subordinate clauses come first in conditional sentences but they are still dependent on the main clause and cannot exist outside of it.
vi: Place
It determine where activities might occur, include where, wherever, and whereas.
For Example:
- I will place my conjunction in the sentence wherever I please.
- The bank is adjacent to the school.
3: Correlative Conjunctions
It is used to tell how two words or phrases in a sentence are associated to each other.
They usually work together to connect two parts of speech.
| Either /Or | I will either go to Karachi or California for holidays. |
| Neither/ Nor | Neither the cats nor the wild hounds would eat the roast he made. |
| Not only/ But also | My new supervisor not only has new ideas but also helps to bring them to life. |
There are three important rules that we need to follow
- Ensure verb agreement
- Ensure pronoun Agreement
- Ensure parallel structure
Rule No 1: Ensure verb agreement
- it Join two singular subjects with a singular verb.
| Incorrect verb agreement | Correct verb agreement |
| Neither the boy nor his sister wants to do their work. | Neither the boy nor his brother want to do their work. |
- it Join two plural subjects with a plural verb.
| In Correct verb agreement | Correct verb agreement |
| Either the students or their parents were as expected to pick up supplies for the project. | Either the students or their parents were expected to pick up supplies for the project. |
- Join a singular subject and a plural subject with the verb form used for the subject closest to the verb.
| In Correct verb agreement | Correct verb agreement |
| Both the Ismail and the Raheem runs two miles every day. | Both the Ismail and the Raheem run two miles every day. |
Rule no 2: Ensuring Pronoun Agreement with Correlative Conjunctions
When two archetypes are used with a correlative conjunction, the rules follow a similar pattern to verb agreement rules. Singular antecedents use singular pronouns, plural antecedents use plural pronouns, and when both a singular or plural antecedent are used, the pronoun is based on the second archetypes or the archetypes closest to the pronoun.
- Both Hareem and Saman completed his part of the work.
- Either the doctors or the nurses will visit their patients at least twice a day.
- Not only the painting but also the sculptures show their unique style when put on display.
Rule no 3: Ensuring Parallel Structure with Correlative Conjunctions
When using correlative conjunctions, it is important that the items or ideas really connected and follow the same grammatical structure.They have to perform equal functions in the sentence so we called this parallel structure.
Parallel structure adds clarity to your writing, making it easier to follow.
For Example
i Non Parallel:
- My sister not only likes to play video games, but also watch dramas.
This example is non parallel because the first conjunction in the pair is followed by a verb, while the second conjunction is followed by a prepositional phrase.
ii Parallel:
- My sister not only likes to play video games, but he also likes to watch dramas.
This example is parallel because both conjunctions are followed by a verb. Separating the conjunction but and also to include the subject.it is an acceptable way to use this conjunction.
Parts of speech and their Types in detail
- Noun Types
- Pronoun Types
- Adjective and its types
- Verb and its Types
- Adverb and its types
- Interjection and its types
- Conjunction and its Types
- Preposition and Its Types