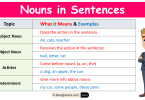
English/Urdu Tenses Proper Guide
Tense /tɛns/ (noun)
The word ‘tense’ is derived from the Latin word ‘tempus’ time. It stipulates the time when an action or event happening, and sometimes the continuation or emptiness of the action.
“A form of verb that allows you to indicate time.”
” فعل کی وہ قسم جو کام کے ہونے کے وقت کو ظاہر کرے”
In English, we use tenses to indicate the past, present, and future, and to differentiate when the work is done in which specific time either in the past, future, or present we divide each tense into further four kinds.
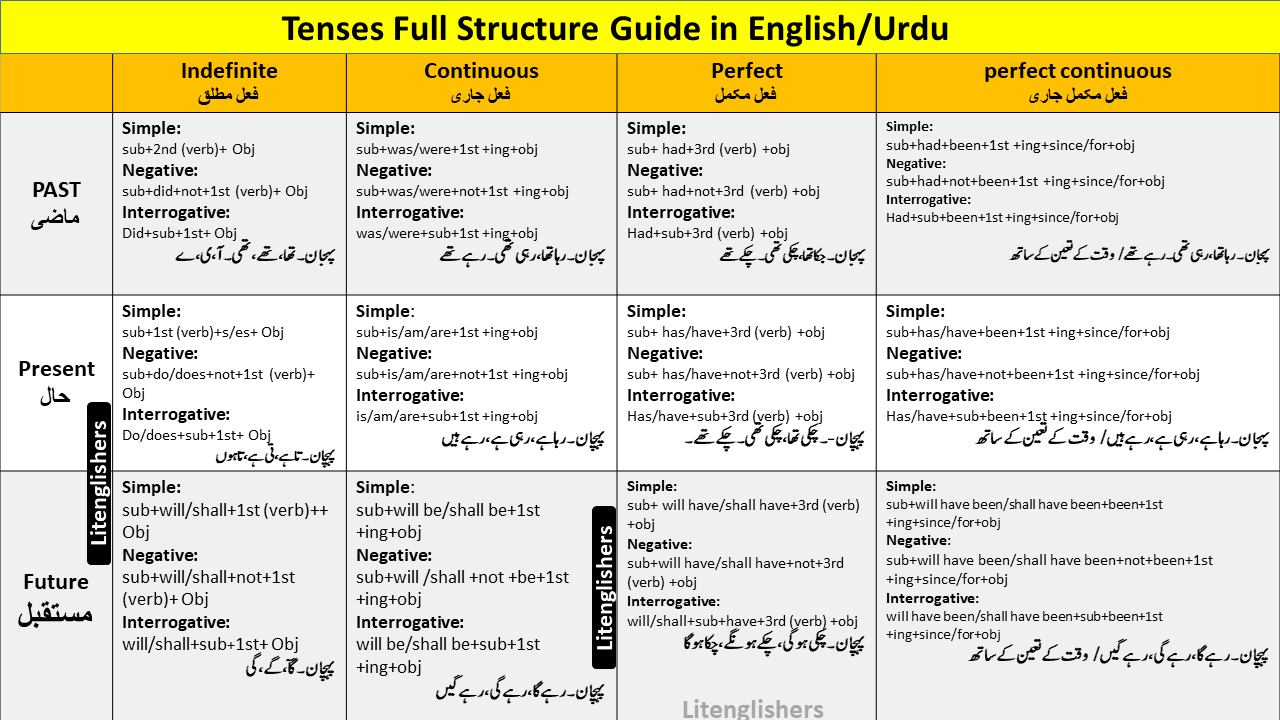
Three main Types of Tenses:
- Past(زمانۂ ماضی )
- Present(زمانۂ مستقبل)
- Future(زمانۂ حال)
1. Past Tense:
“An activity or event happened in the past or time (when & where) or past state of being .”
sentence formation: Past Tense is cleaved into further four sub-types…
| Past Indefinite
(فعل ماضی مطلق) پہجان۔ تھا،تھے،تھی۔آ،ی،ے |
past continuous
(فعل ماضی جاری) پہجان۔ رہا تھا،رہی تھی۔ رہے تھے |
past perfect
(فعل ماضی مکمل) پہجان۔ جکا تھا،چکی تھی۔ چکے تھے |
past perfect continuous
(فعل ماضی مکمل جاری) پہجان۔ رہا تھا،رہی تھی۔ رہے تھے / وقت کے تعین کے سا تھ |
|
| Simple | sub+2nd (verb)+ Obj | sub+was/were+1st +ing+obj | sub+ had+3rd (verb) +obj | sub+had+been+1st +ing+since/for+obj |
| Negative | sub+did+not+1st (verb)+ Obj | sub+was/were+not+1st +ing+obj | sub+ had+not+3rd (verb) +obj | sub+had+not+been+1st +ing+since/for+obj |
| Interrogative | Did+sub+1st+ Obj | was/were+sub+1st +ing+obj | Had+sub+3rd (verb) +obj | Had+sub+been+1st +ing+since/for+obj |
Example sentences :
- we met yesterday.
- we did not meet yesterday.
- Did we meet yesterday?
- we were playing.
- we were not playing.
- were we playing?
- we had lived in New York.
- we had not lived in New York.
- Had we lived in New York?
- we had been playing games for six hours when Dad came home.
- we had not been waiting for her since morning.
- Had we waited for her for six hours?
Present Tense :
“Used to tell about the events happening now, habitually performed and the state that currently exists.”
Structure: The Present Tense is sliced up into four further kinds
| Present Indefinite
(فعل حال مطلق) پہچان۔ تا ہے ،تی ہے،تا ہوں |
Present continuous
(فعل حال جاری) پہچان۔ رہا ہے، رہی ہے، رہے ہیں |
Present perfect
( فعل حال مکمل) پہچان-۔چکی تھا، چکی تھی۔ چکے تھے۔ |
Present perfect continuous
(فعل حال مکمل جاری) پہجان۔ رہا ہے، رہی ہے، رہے ہیں/ وقت کے تعین کے سا تھ |
|
| Simple | sub+1st (verb)+s/es+ Obj | sub+is/am/are+1st +ing+obj | sub+ has/have+3rd (verb) +obj | sub+has/have+been+1st +ing+since/for+obj |
| Negative | sub+do/does+not+1st (verb)+ Obj | sub+is/am/are+not+1st +ing+obj | sub+ has/have+not+3rd (verb) +obj | sub+has/have+not+been+1st +ing+since/for+obj |
| Interrogative | Do/does+sub+1st+ Obj | is/am/are+sub+1st +ing+obj | Has/have+sub+3rd (verb) +obj | Has/have+sub+been+1st +ing+since/for+obj |
Example sentences :
- she lives in Korea.
- she does not live in Korea.
- Does she live in Korea?
- she is going to Korea.
- They are not going to Korea.
- Am I going to Korea?
- I have Planned to go to Korea.
- I have not planned to go to Korea.
- Have they planned to go to Korea?
- I have been planning to go to Korea since 2023.
- She has not been planning to go to Korea since 2023.
- Has she been planning to go to Korea for two hours?
Future Tense:
” used to describe an action or event that has not happened yet but has in prospect to happen in future.”
Structure: Future tense is sliced up into four further kinds
| Future Indefinite
(فعل مستقبل مطلق) پہچان۔ گآ، گے ، گی |
Future continuous
(فعل مستقبل جاری) پہچان۔ رہے گا، رہے گی، رہے گیں |
Future perfect
(فعل مستقبل مکمل) پہچان۔ چکی ہوگی، چکے ہونگے،چکا ہوگا |
Future perfect continuous
(فعل مستقبل مکمل جاری) پہچان۔ رہے گا، رہے گی، رہے گیں/ وقت کے تعین کے سا تھ |
|
| Simple | sub+will/shall+1st (verb)++ Obj | sub+will be/shall be+1st +ing+obj | sub+ will have/shall have+3rd (verb) +obj | sub+will have been/shall have been+been+1st +ing+since/for+obj |
| Negative | sub+will/shall+not+1st (verb)+ Obj | sub+will /shall +not +be+1st +ing+obj | sub+will have/shall have+not+3rd (verb) +obj | sub+will have been/shall have been+not+been+1st +ing+since/for+obj |
| Interrogative | will/shall+sub+1st+ Obj | will be/shall be+sub+1st +ing+obj | will/shall+sub+have+3rd (verb) +obj | will have been/shall have been+sub+been+1st +ing+since/for+obj |
Example sentences:
- He will come.
- He will not come today.
- Will he come today?
- He will be here soon.
- He will not be going to Lahore.
- Will he be doing his work?
- I shall have postponed the meeting.
- we will not have gone to Lahore.
- will we have to cursed him?
- He will have waiting for me since 2 days.
- He will not have waiting for me since 2 days.
- Will he have waiting for me for 2 hours?
| Tip.
Note! According to the view of many grammarians there are only two tenses in English:
That is because we make those two tenses with the verb alone – he eats/he ate. They do not consider that he will eat/ he is eating or he has eaten (for example) are tenses because they are not formed solely from the verb “eat”. For English learners, most EFL teachers and books treat all these constructions as tenses. |
we cannot talk of tenses without considering two components (time and situation)
Time indicate:
- past- before/now
- present- Now and continuous time where we use Now
- Future- after/ Now
Situation indicate:
- Perfective– complete action / state
- progressive – uncomplete actions
Here is the real time representation of how these components work adjacently to create basic tenses.
| Time | ||||
| past | present | future | ||
| Simple ( No standpoint) | ate | eats | will wat | |
| Situation | Perfective | had eaten | has eaten | will have eaten |
| progressive | was eating | is eating | will be eating | |
Click here for the detailed piece of information of Tenses