In English, we often use two ways of writing sentences: Active Voice and Passive Voice. Both are correct, but their use depends on what we want to focus on. This article will explain active and passive voice in easy wording, with clear structures and 50 useful examples.
What is Active and Passive Voice?
Active Voice → The subject does the action.
Passive Voice → The subject receives the action.
Example:
- Active → She delivers the letters.
- Passive → The letters are delivered.
So, in active voice we highlight who does the work, and in passive voice we highlight what happens to the object.
Structures of Active and Passive Voice
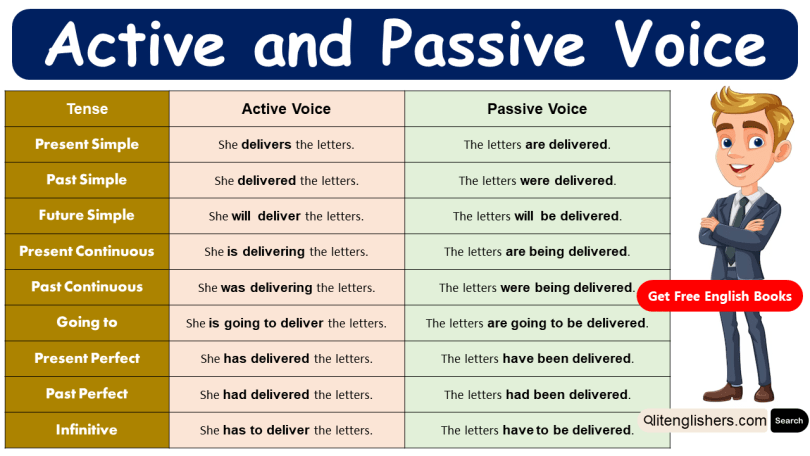
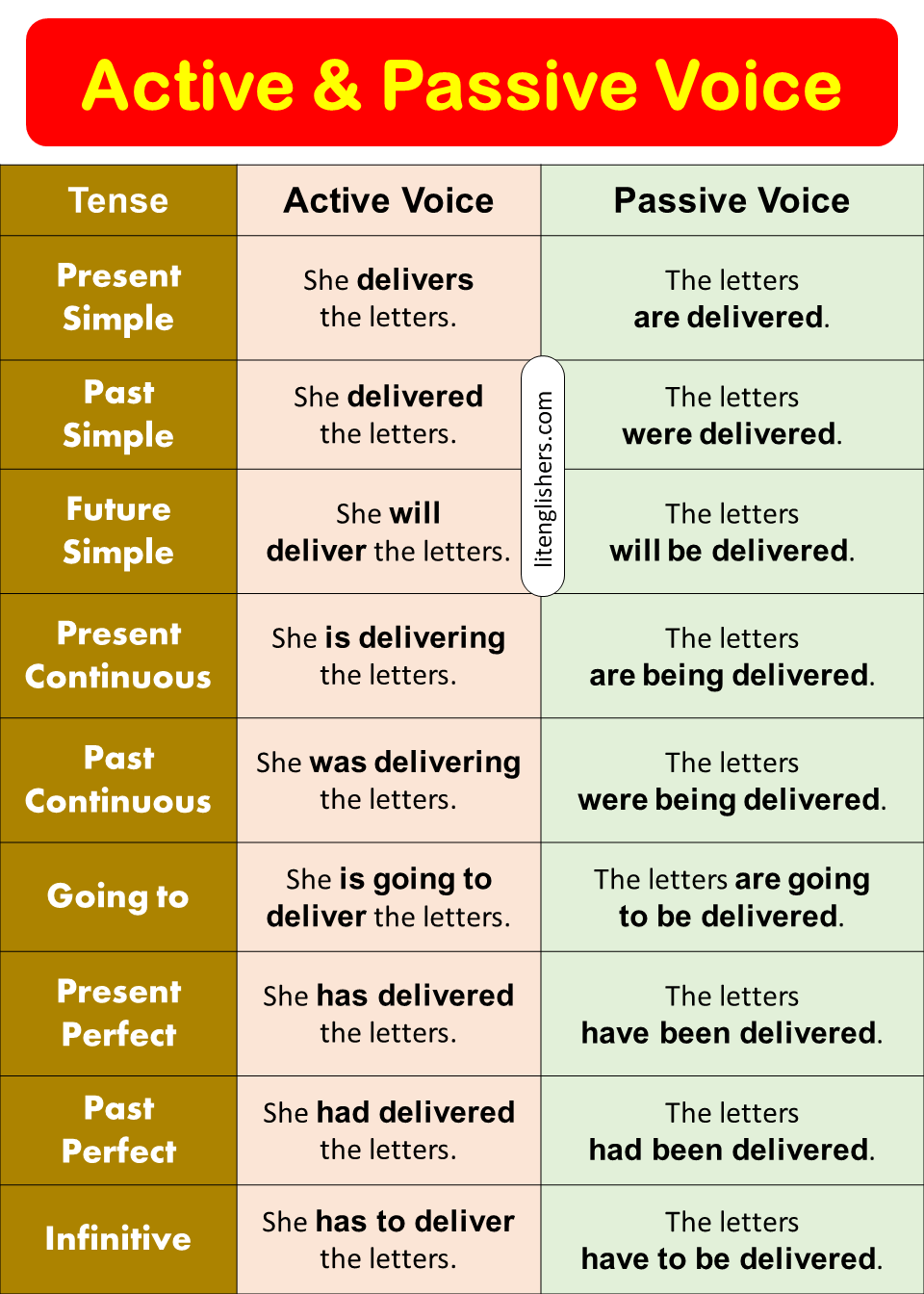
Here are some common tense structures before we look at examples:
| Tense | Active Voice Structure | Passive Voice Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | Subject + Verb + Object | Object + is/are + Past Participle |
| Past Simple | Subject + Verb (2nd form) + Object | Object + was/were + Past Participle |
| Future Simple | Subject + will + Verb + Object | Object + will be + Past Participle |
| Present Continuous | Subject + is/are + Verb+ing + Object | Object + is/are + being + Past Participle |
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + Verb+ing + Object | Object + was/were + being + Past Participle |
| Present Perfect | Subject + has/have + Past Participle + Object | Object + has/have + been + Past Participle |
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + Past Participle + Object | Object + had + been + Past Participle |
| Infinitive | Subject + has to + Verb + Object | Object + has to be + Past Participle |
Examples of Active and Passive Voice
1. Present, Past, and Future Tenses
Present Simple
- Active → She delivers the letters.
- Passive → The letters are delivered.
Past Simple
- Active → She delivered the letters.
- Passive → The letters were delivered.
Future Simple
- Active → She will deliver the letters.
- Passive → The letters will be delivered.
Present Continuous
- Active → She is delivering the letters.
- Passive → The letters are being delivered.
Past Continuous
- Active → She was delivering the letters.
- Passive → The letters were being delivered.
Present Perfect
- Active → She has delivered the letters.
- Passive → The letters have been delivered.
Past Perfect
- Active → She had delivered the letters.
- Passive → The letters had been delivered.
Future (Going to)
- Active → She is going to deliver the letters.
- Passive → The letters are going to be delivered.
Infinitive Form
- Active → She has to deliver the letters.
- Passive → The letters have to be delivered.
2. Daily Life Examples
Active → The teacher teaches English.
Passive → English is taught by the teacher.
Active → They play football in the park.
Passive → Football is played in the park.
Active → The chef cooked dinner.
Passive → Dinner was cooked by the chef.
Active → He writes a story.
Passive → A story is written by him.
Active → We celebrated the festival.
Passive → The festival was celebrated by us.
Active → The manager will approve the plan.
Passive → The plan will be approved by the manager.
Active → She sings a beautiful song.
Passive → A beautiful song is sung by her.
Active → They helped the poor.
Passive → The poor were helped by them.
Active → He has repaired the car.
Passive → The car has been repaired by him.
Active → She will invite the guests.
Passive → The guests will be invited by her.
3. Mixed Context Examples
Active → People speak English worldwide.
Passive → English is spoken worldwide.
Active → The workers are building a bridge.
Passive → A bridge is being built by the workers.
Active → She washed the clothes yesterday.
Passive → The clothes were washed yesterday.
Active → He is writing a letter.
Passive → A letter is being written by him.
Active → They had finished the project.
Passive → The project had been finished by them.
Active → We will watch the movie tomorrow.
Passive → The movie will be watched tomorrow.
Active → She paints the walls.
Passive → The walls are painted by her.
Active → He is going to clean the room.
Passive → The room is going to be cleaned by him.
Active → The company will launch a new product.
Passive → A new product will be launched by the company.
Active → They are planting trees.
Passive → Trees are being planted by them.
Quick Recap
- Active Voice → Subject does the action.
- Passive Voice → Subject receives the action.
- Use passive voice when action is more important than the doer.
Summary of Active and Passive Voice Article
This article explains Active and Passive Voice in easy English for learners. Active voice shows that the subject does the action, while passive voice shows that the subject receives the action. Clear structures, tables, and 50 examples are given to show the difference in different tenses and daily life sentences.
Example:
- Active → She delivers the letters.
- Passive → The letters are delivered.
The article also provides quick rules, mixed examples, and FAQs to help learners understand when to use active or passive voice. Active voice is direct and simple, while passive voice is used when the action or object is more important than the doer.
FAQs
What is active voice in English?
Active voice is when the subject performs the action. Example: She writes a letter.
What is passive voice in English?
Passive voice is when the subject receives the action. Example: A letter is written by her.
Why do we use passive voice?
We use passive voice to focus on the action or object instead of the doer.
Can all sentences be changed into passive voice?
No, only sentences with an object can be changed into passive voice.
Which is better: active or passive voice?
Both are correct. Active voice is clearer and direct, while passive voice is used when the doer is unknown or less important.
Read More