Nouns Examples and definition
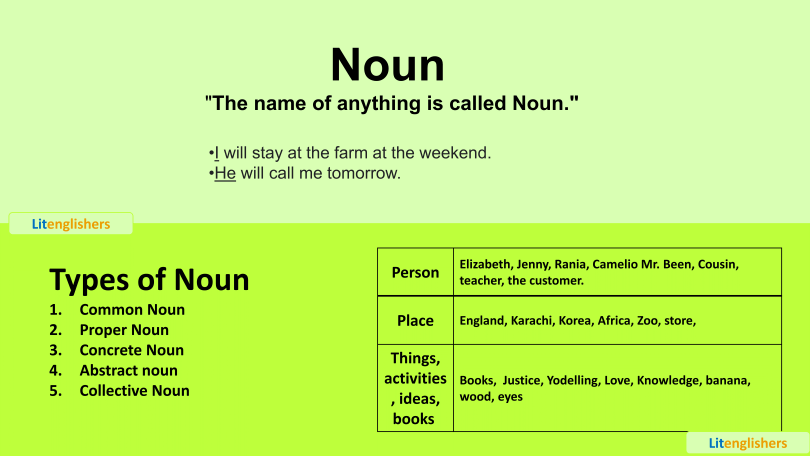
“The name of anything is called Noun.”
Put simply all the things that belong to the world is considered to be a noun. It could be anyone, whether you are talking about a human, animal, angel, ghost, monkey, fox, love, hatred, friendship, self-preservation, and Cleopatra.
It’s like the bread and butter of our speech.
Noun Examples:
| Person | Elizabeth, Jenny, Raheema, Charlie, Mr. Been, Cousin, teacher, the customer. |
| Place | England, Karachi, Korea, Africa, Zoo, store, |
| Things, activities, ideas, books | Books, Justice, Yodelling, Love, Knowledge, banana, wood, eyes |
In a sentence, a noun can play the role of a:
- subject
- Indirect Object
- Direct Object
- Subject complement
- object complement
- Appositive
- Adjective
 Types of Noun and noun examples:
Types of Noun and noun examples:
- Common Noun
- Proper Noun
- Concrete Noun
- Abstract noun
- Collective Noun
Common nouns and Proper nouns are the basic types of nouns. You use both types of nouns to refer to different people, places, things, and ideas.
1: Common Noun
“A common noun refers to a non-specific or generic person, place, idea, or thing rather than specific ones.”
Common noun examples:
Teacher, movie, state, island, friend, dog, country, girl, boy, children.
- These words are non-specific nouns and can be referring to any island, any girl/boy/children, or any country. Common nouns are not usually capitalized when they appear at the beginning of a sentence. As the common nouns in the following sentence are not capitalized.
1: My brother and his friend decided to buy candy from the bazaar.
2: My favorite pets are dogs, cats, and lizards.
3: The girls solved the maths problems quickly.
The four common nouns in this sentence (brother, friend, candy, bazaar) are not capitalized, because they are not referring to any specific person, thing, or place.
2: Proper Noun
“Proper Noun generally refers to a specific person, place, or thing and are usually capitalized.”
A name is a noun but when we use it for pretty special things, persons, or places then we named it a proper noun.
Proper noun examples: John, Harry, England, London, Ford, Sony, Amazon, WordPress, Titanic. Manifestly we use a capital letter for the first letter of a proper noun.
1: I live in Pakistan.
2: The last day in July is a Sunday.
3: She works for Ahad.
The words ( Pakistan, July, and Ahad) start with a capital letter.
3: Concrete Noun
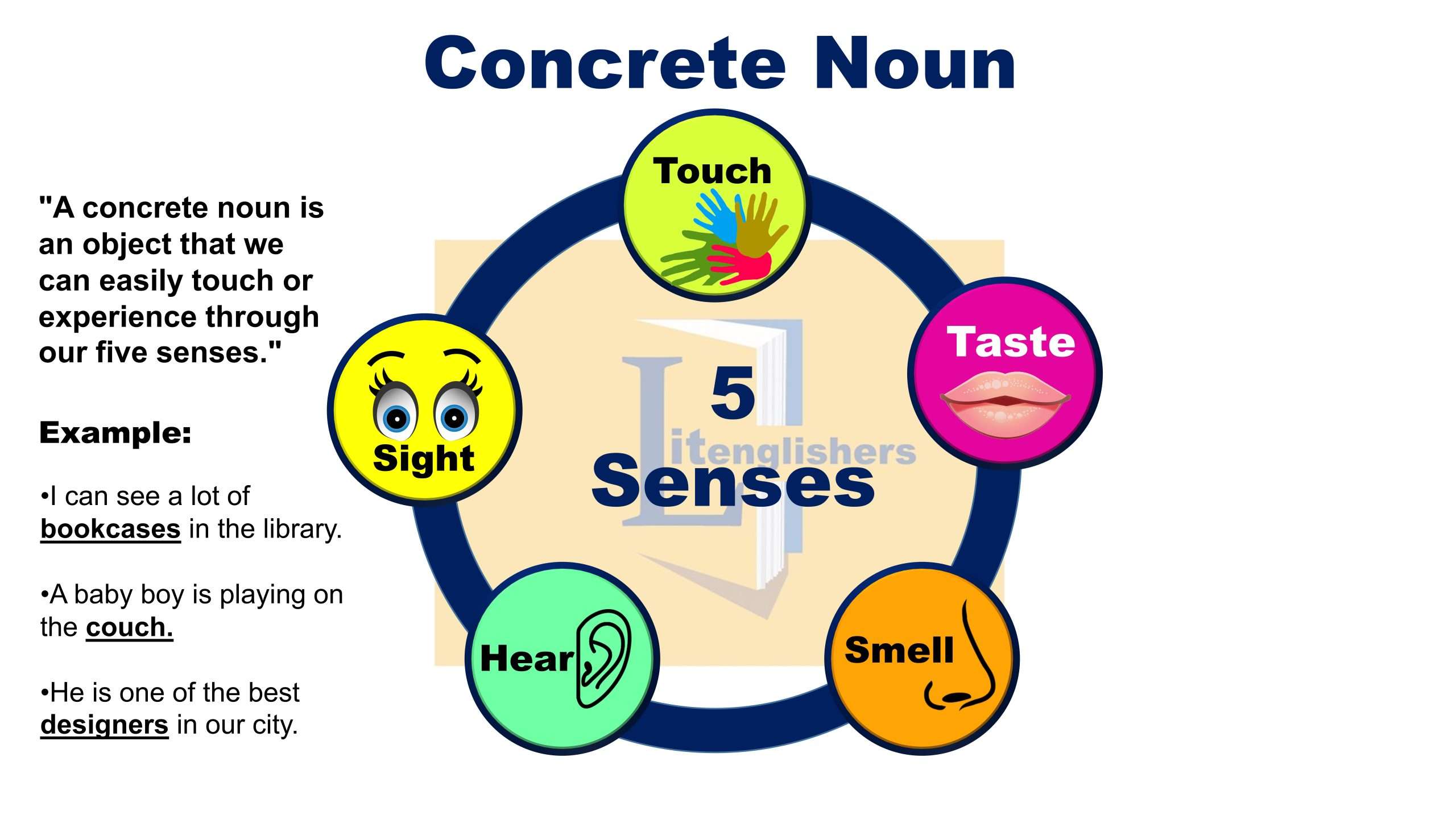
“A concrete noun is an object that we can easily touch or experience through our five senses.”
Concrete noun examples: Book, chair, house, automobile, choir, cakes, bile, etc
A book is a concrete noun because it can be seen, smelled, and touched. A song is also a concrete noun because it can be heard.
- I can see a lot of bookcases in the library.
- A baby boy is playing on the couch.
- He is one of the best designers in our city.
 Concrete nouns come into two forms:
Concrete nouns come into two forms:
1: Common nouns: that allude to ordinary places, things, and people. Like (girl, mall, quilt, bottle)
2: Proper nouns: that allude to particular places, things, and people. For instance, (New York City, and Chicago Cubs).
Habitually common nouns are not capitalized, while proper nouns are capitalized.
4: Abstract Noun
“A noun that instead of physical touch, names an idea, quality, event, or notion is known as a concrete noun.”
It bespoke something immaterial and abstract that we can’t experience with our five senses. We can’t see, smell, or touch abstract nouns.
Abstract noun examples:
Courage, freedom, anger, joy, fear, desire, creativity, love, patience, progress, excellence, and friendship.
- The entire crew is celebrating their victory.
- This hostel is known for its strictness.
Abstract nouns don’t refer to people or places, because people and places are real things that exist on earth. We can’t eat, drink or touch the given abstract nouns we just feel them.
5: Collective Noun
“The collection of individuals is called a collective noun.”
It refers to several people or things, such as the senate, company, party, audience, committee, jury, or army.
- A team of eleven football players.
- A crew of hundred pilots.
- A family and five children.
Many collective nouns are common nouns but sometimes they can also act to be proper nouns when they refer to the name of a company or organization with more than one person.
For Instance:
Sony, Microsoft, WHO, FBI, Manchester United, the BBC, Apple, and CNN.
What are the Jobs Nouns do in a sentence?
In the elementary grades, students learn that nouns are words that represent a person, place, thing, or idea. As grammar concepts become more complex in middle and high school, students need to know more about nouns. Knowing exactly what “job” a noun does in a sentence will help with the language problems students face in higher grades. Students must know the function of a noun in a sentence to use the case of the proper pronoun. Students who understand the different functions of nouns will also be more successful in learning foreign languages.
1: Subjects and predicate noun examples ( Nominative)
Nouns are frequently used as the subject of a sentence. The subject states who or what the sentence is about. More complicated thing is to detect a predicate noun, which is also known as a predicate nominative.
“A predicate nominative is a noun in a predicate that retitled the subject.
For Instance
- “My brother is a cook”,
In this sentence the subject is “brother” and the predicate nominative is “cook“. Predicate nominatives are only spotted in sentences that have linking verbs rather than action verbs.
2: Direct and Indirect Objects
Nouns execute the role of a direct or indirect object in a sentence.
i: Direct Object
A direct object endured the action of a transitive verb and answer the questions like “what?” or “who?” about the verb.
For instance:
In the sentence, “Lisa threw a ball,” the transitive verb is “threw.” If you ask, “Lisa threw what?” The answer, “ball,” is the direct object.
ii: Indirect Object
An indirect object will only be spotted in a sentence that contains a direct object, and tells “who” or “what” received the direct object.
For instance:
In the sentence, “Lisa” threw Lisa the ball,” we already know that “ball” is the direct object.” If you ask, “Who received the ball?” we find the indirect object, “Lisa.”
3: Appositives
“An appositive is a noun that pursues another noun and gave a name again, identifies or explicates that noun.”
For example:
In the sentence “My brother Umar is a chef,” “Umar” is an appositive because it follows the noun “brother” and explicates the brother as “Bill.” Appositives can also be found within appositive phrases surrounded by modifiers.
For example:
In the sentence “My dog, a lazy but friendly golden Siberian Husky always greets me at the door when I arrive at the shop,” the appositive is “Siberian Husky” found within the appositive phrase “a lazy but friendly “Golden Siberian Husky.”
4: Preposition
Objects of prepositions are spotted in prepositional phrases, which start with a preposition and end with a noun. Prepositions show a relationship between the object and another word in the sentence.
For example:
In the sentence, “Lisa put his shoes in the box,” the word “in” is the preposition, and the noun “box” is the object of the preposition. “In” shows the relationship between the closet and Lisa’s shoes. Therefore, the phrase “in the box” is considered a prepositional phrase.
Parts of speech and their Types in detail
- Noun Types
- Pronoun Types
- Adjectives and their types
- Verbs and their Types
- Adverbs and their types
- Interjection and its types
- Conjunction and its Types
- Preposition and Its Types