Regular verbs are essential in English, especially for forming sentences in the past tense. Regular verbs follow a specific pattern, making it easy for learners to recognize and apply them in different contexts. In this post, we’ll cover what regular verbs are, how to form their past tense, the difference between regular and irregular verbs, a comprehensive list of common regular verbs, and an exploration of why regular verbs are also called “weak verbs.”
What is a Regular Verb?
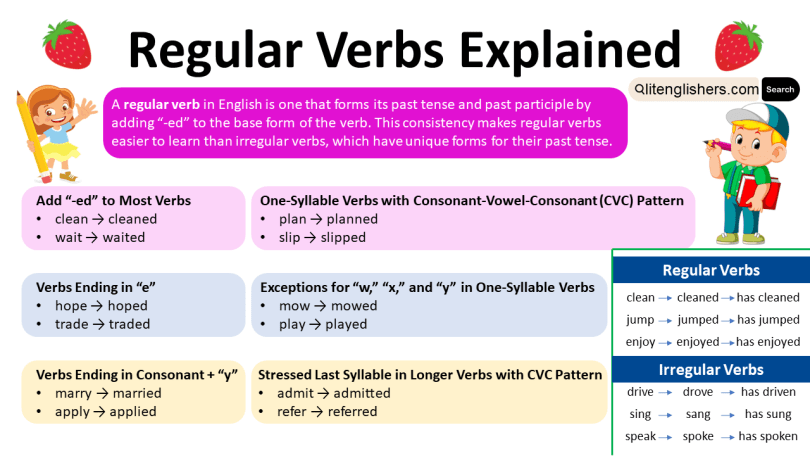
A regular verb in English is one that forms its past tense and past participle by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb. This consistency makes regular verbs easier to learn than irregular verbs, which have unique forms for their past tense.
For instance:
- Base form: walk
- Past tense: walked
- Past participle: walked
This structure is predictable and helps learners apply the rule to other verbs that follow the same pattern.
Creating the Past Forms of Regular Verbs
Creating the Past Forms of Regular Verbs
- Add “-ed” to Most Verbs
- Example: clean → cleaned
- Example: wait → waited
- One-Syllable Verbs with Consonant-Vowel-Consonant (CVC) Pattern
If a one-syllable verb ends with a consonant-vowel-consonant (CVC), double the final consonant and add “-ed.”- Example: plan → planned
- Example: slip → slipped
- Exceptions for “w,” “x,” and “y” in One-Syllable Verbs
If the final consonant is “w,” “x,” or “y,” do not double it.- Example: mow → mowed
- Example: play → played
- Example: fix → fixed
- Stressed Last Syllable in Longer Verbs with CVC Pattern
When the last syllable of a longer verb is stressed and ends in a consonant-vowel-consonant, double the last consonant and add “-ed.”- Example: admit → admitted
- Example: refer → referred
- Unstressed Last Syllable in Longer Verbs with CVC Pattern
If the first syllable is stressed in a longer verb ending with CVC, just add “-ed” without doubling the final consonant.- Example: listen → listened
- Example: answer → answered
- Verbs Ending in “e”
If a verb ends with “e,” simply add “d.”- Example: hope → hoped
- Example: trade → traded
- Verbs Ending in Consonant + “y”
When a verb ends with a consonant followed by “y,” change the “y” to “i” and add “-ed.”- Example: marry → married
- Example: apply → applied
Regular vs. Irregular Verbs
Regular and irregular verbs differ in how they form their past tenses and past participles.
Regular Verbs
With regular verbs, the simple past tense and past participle are formed by adding “-ed” to the base form. The simple past and past participle forms are the same.
| Regular Verb | Simple Past Tense | Past Participle |
| clean | cleaned | has cleaned |
| jump | jumped | has jumped |
| enjoy | enjoyed | has enjoyed |
| watch | watched | has watched |
| walk | walked | has walked |
These examples illustrate how regular verbs maintain a consistent structure in both the simple past and past participle forms.
Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs, on the other hand, do not follow a standard rule for forming the simple past and past participle. The past forms of irregular verbs may be the same or different.
Irregular Verbs with Different Simple Past and Past Participle Forms
| Irregular Verb | Simple Past Tense | Past Participle |
| drive | drove | has driven |
| sing | sang | has sung |
| speak | spoke | has spoken |
| write | wrote | has written |
| fly | flew | has flown |
- These verbs change their forms completely between the base, simple past, and past participle.
Irregular Verbs with the Same Simple Past and Past Participle Forms
Some irregular verbs keep the same form in both the simple past and past participle but differ from the base form.
| Irregular Verb | Simple Past Tense | Past Participle |
| bring | brought | has brought |
| think | thought | has thought |
| teach | taught | has taught |
| catch | caught | has caught |
| leave | left | has left |
These examples demonstrate the variety in how irregular verbs form past tenses, contrasting sharply with the predictable pattern of regular verbs.
Regular Verbs List
To assist learners, here’s a helpful list of some common regular verbs that you’ll likely encounter in daily English:
| Base Form | Past Tense | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| ask | asked | asked |
| clean | cleaned | cleaned |
| help | helped | helped |
| jump | jumped | jumped |
| listen | listened | listened |
| love | loved | loved |
| move | moved | moved |
| talk | talked | talked |
These regular verbs follow the same rule of adding “-ed” for past forms, making them reliable for new English learners.
Regular Verbs Are Weak Verbs
In linguistic terms, regular verbs are often referred to as weak verbs. This classification comes from the fact that they do not change form dramatically or “strongly” as irregular verbs do. Instead, they follow a “weak” pattern, consistently adding “-ed” without modifying the verb’s core structure.
For example:
- Regular (weak): Work → worked
- Irregular (strong): Run → ran
The consistency of weak verbs in English offers a reliable pattern for language learners to understand and apply.
You May Also Like
- Common Mistakes in English
- Formal and Informal Words list
- Use of Modal Verbs Will and Shall
- Vertebrates and Invertebrates Names