Learning English can feel like a big challenge, especially when it comes to understanding grammar and vocabulary. But don’t worry—every expert was once a beginner! In this article, we’ll break down the essentials of English grammar, including the eight parts of speech and their role in forming sentences. Whether you’re just starting out or brushing up on your skills, this guide is designed to make learning simple, engaging, and effective. Let’s explore and unlock the building blocks of the English language together!
In this article, we are not going to learn about the main types of word classes. Here, we will talk about their types along with their helpful examples and short usages of each. The pattern of this lesson is given below:
First of all, we will know the eight parts of speech names, then their types along with their examples. Learning these examples without comprehensive explanations, you can easily improve your grammar and vocabulary in English.
Word Classes
Word classes are also known as parts of speech in the English language. There are eight main types of word classes, and we are going to learn about nine types. We are going to do our best to help you improve your grammar and vocabulary in the English language. All are explained below; let’s learn…
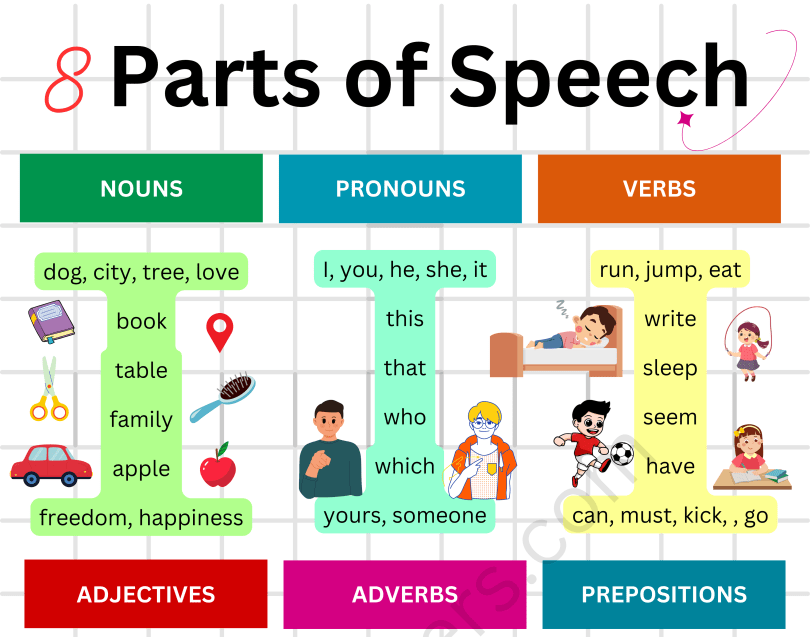
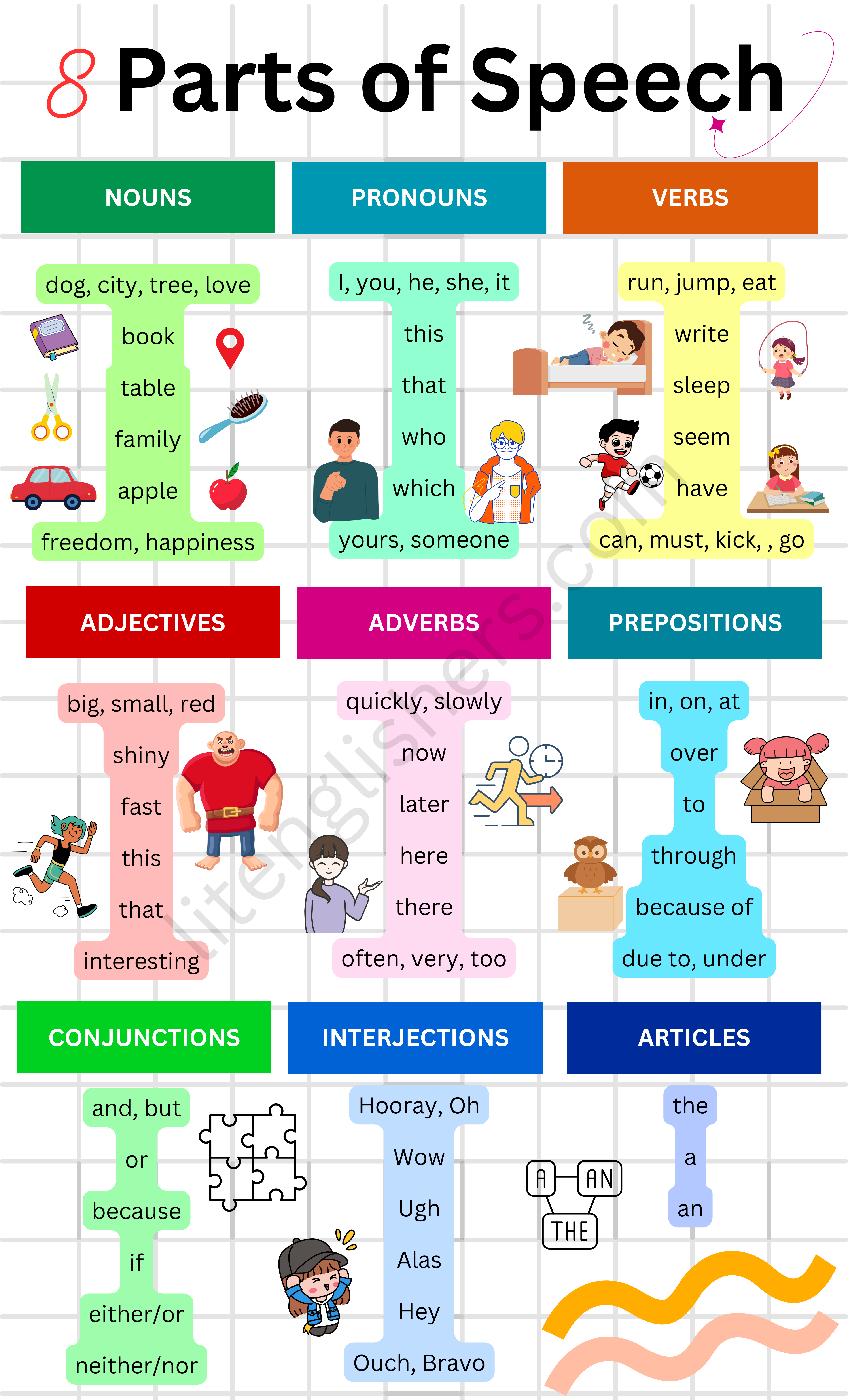
NOUNS
- Common Nouns
- Proper Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Collective Nouns
- Countable Nouns
- Uncountable Nouns
PRONOUNS
- Personal Pronouns
- Possessive Pronouns
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Relative Pronouns
- Interrogative Pronouns
- Indefinite Pronouns
VERBS
- Action Verbs
- Linking Verbs
- Auxiliary Verbs
- Modal Verbs
- Transitive Verbs
- Intransitive Verbs
ADJECTIVES
- Descriptive Adjectives
- Quantitative Adjectives
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Possessive Adjectives
- Interrogative Adjectives
- Comparative Adjectives
- Superlative Adjectives
ADVERBS
- Adverbs of Manner
- Adverbs of Time
- Adverbs of Place
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Degree
PREPOSITIONS
- Prepositions of Time
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Direction/Movement
- Prepositions of Cause/Reason/Purpose
CONJUNCTIONS
- Coordinating Conjunctions
- Subordinating Conjunctions
- Correlative Conjunctions
INTERJECTIONS
- Greeting
- Joy
- Surprise
- Approval
- Anger or Frustration
- Sadness or Pain
- Calling Attention
- Hesitation
ARTICLES
- Definite Article
- Indefinite Articles
Parts of Speech Examples
1. NOUNS
Types of Nouns:
Common Nouns: Refer to general things.
- Examples: cat, dog, city, book, car, house
Proper Nouns: Refer to specific names (capitalized).
- Examples: John, London, Microsoft, Amazon, Eiffel Tower
Concrete Nouns: Refer to tangible things.
- Examples: apple, table, phone, water, tree
Abstract Nouns: Refer to ideas or feelings.
- Examples: love, happiness, freedom, truth, justice
Collective Nouns: Refer to groups.
- Examples: team, family, herd, flock, audience
Countable Nouns: Can be counted.
- Examples: pen, chair, child, star, flower
Uncountable Nouns: Cannot be counted.
- Examples: milk, sugar, air, information, furniture
2. PRONOUNS
Types of Pronouns:
Personal Pronouns: Represent people or things.
- Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they, me, him, her, us, them
Possessive Pronouns: Show ownership.
- Examples: mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs
Reflexive Pronouns: Refer back to the subject.
- Examples: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves
Demonstrative Pronouns: Point out specific things.
- Examples: this, that, these, those
Relative Pronouns: Link clauses or phrases.
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, that
Interrogative Pronouns: Used for questions.
- Examples: who, whom, whose, what, which
Indefinite Pronouns: Refer to unspecified things.
- Examples: someone, anyone, everyone, nobody, nothing, each, all, many, few, some
3. VERBS
Types of Verbs:
Action Verbs: Show actions.
- Examples: run, jump, eat, write, read, sing, walk
Linking Verbs: Connect the subject to a description.
- Examples: is, am, are, was, were, seem, appear, become
Helping (Auxiliary) Verbs: Assist the main verb.
- Examples: is, am, are, was, were, have, has, had, do, does, did, will, shall, can, may
Modal Verbs: Express ability, possibility, or necessity.
- Examples: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would
Transitive Verbs: Require an object.
- Examples: kick, eat, watch, bring, take
Intransitive Verbs: Do not require an object.
- Examples: sleep, run, arrive, go, exist
4. ADJECTIVES
Types of Adjectives:
Descriptive Adjectives: Describe qualities.
- Examples: big, small, red, blue, shiny, heavy
Quantitative Adjectives: Indicate quantity.
- Examples: some, many, few, several, one, two
Demonstrative Adjectives: Point out specific items.
- Examples: this, that, these, those
Possessive Adjectives: Show ownership.
- Examples: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
Interrogative Adjectives: Ask questions.
- Examples: which, what, whose
Comparative Adjectives: Compare two things.
- Examples: bigger, smaller, faster, more interesting
Superlative Adjectives: Indicate the highest degree.
- Examples: biggest, smallest, fastest, most interesting
5. ADVERBS
Types of Adverbs:
Adverbs of Manner: Describe how something happens.
- Examples: quickly, slowly, happily, badly
Adverbs of Time: Indicate when something happens.
- Examples: now, later, yesterday, tomorrow
Adverbs of Place: Indicate location.
- Examples: here, there, everywhere, nowhere
Adverbs of Frequency: Indicate how often.
- Examples: always, often, never, rarely
Adverbs of Degree: Indicate intensity.
- Examples: very, too, quite, almost, completely
6. PREPOSITIONS
Types of Prepositions:
Prepositions of Time: Indicate time.
- Examples: at, on, in, during, before, after
Prepositions of Place: Indicate location.
- Examples: in, on, at, under, over, between
Prepositions of Direction/Movement: Indicate direction.
- Examples: to, into, onto, through, towards
Prepositions of Cause/Reason/Purpose: Indicate reasons.
- Examples: because of, due to, for, since
7. CONJUNCTIONS
Types of Conjunctions:
Coordinating Conjunctions: Connect equal parts.
- Examples: and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet
Subordinating Conjunctions: Connect dependent and independent clauses.
- Examples: because, although, while, since, if, when, after, before
Correlative Conjunctions: Work in pairs.
- Examples: either/or, neither/nor, both/and, not only/but also
8. INTERJECTIONS
1. Interjections for Greeting
Used to greet someone.
Examples:
- Hello!
- Hi!
- Hey!
- Good morning!
2. Interjections for Joy
Express happiness, excitement, or pleasure.
Examples:
- Hooray!
- Yay!
- Wow!
- Hurrah!
3. Interjections for Surprise
Show astonishment or sudden realization.
Examples:
- Oh!
- Ah!
- Wow!
- Whoa!
- What!
4. Interjections for Approval
Express praise or appreciation.
Examples:
- Bravo!
- Well done!
- Amazing!
- Good job!
5. Interjections for Anger or Frustration
Express annoyance or irritation.
Examples:
- Ugh!
- Damn!
- Argh!
- Tsk-tsk!
6. Interjections for Sadness or Pain
Show grief, sorrow, or discomfort.
Examples:
- Alas!
- Oh no!
- Ouch!
- Ah!
7. Interjections for Calling Attention
Used to grab someone’s attention.
Examples:
- Hey!
- Listen!
- Look!
- Yo!
8. Interjections for Hesitation
Indicate uncertainty or hesitation.
Examples:
- Uh…
- Um…
- Er…
- Hmm…
9. ARTICLES
Types of Articles:
Definite Article: Refers to something specific.
- Examples: the
Indefinite Articles: Refer to something non-specific.
- Examples: a, an
Examples Summary
Here’s the simplified table with just the main parts of speech and their collected examples:
| Part of Speech | Examples |
|---|---|
| Nouns | dog, city, apple, happiness, family, tree, freedom, love, book, table |
| Pronouns | I, you, he, she, it, we, they, mine, yours, this, that, who, which, someone, nobody |
| Verbs | run, jump, eat, write, is, seem, have, can, must, kick, sleep, go |
| Adjectives | big, small, red, shiny, interesting, heavy, fast, many, this, that |
| Adverbs | quickly, slowly, now, later, here, there, always, often, very, too |
| Prepositions | in, on, at, under, over, to, through, because of, due to |
| Conjunctions | and, but, or, because, if, either/or, neither/nor |
| Interjections | Hooray, Oh, Bravo, Ugh, Alas, Hey, Wow, Ouch |